Research Institution Counterpoint pointed out that one-third of smartphone SoCs will be advanced by 3 nm or 2 nm in 2026. With the popularity of generative AI mobile phones and the increase in demand for high-performance and low-power processing capabilities, the overall process upgrade is accelerating.
Counterpoint's latest "Long-term Forecast of Global Mobile Processor (AP-SoC) Points" report pointed out that Apple will first adopt 3 nm points in 2025, and it is expected that more than 80% of its products will be introduced into this technology. By 2026, Apple, Qualcomm and Joint Development Corporation will also continue to adopt NT$2 nanometers. At the time, 5/4 nanometers will become the most popular processing point in smart phones, accounting for more than one-third of the overall SoC shipment.
Apple was the first to introduce TECHNOLOGY 3-nanometer A17 Pro chips in the iPhone 15 Pro series in 2023; Qualcomm and Joint Development Technology launched its 3-nanometer flagship SoC in 2024. Starting from 2025, all new generation flagship SoCs will be fully converted to 3 nm. The 3-nanometer and 2-nanometer processes not only provide higher transistor density and temporal speed, but also support generative AI, immersive games and high-quality image processing and become the key to improving the efficiency and efficiency of smart phones.
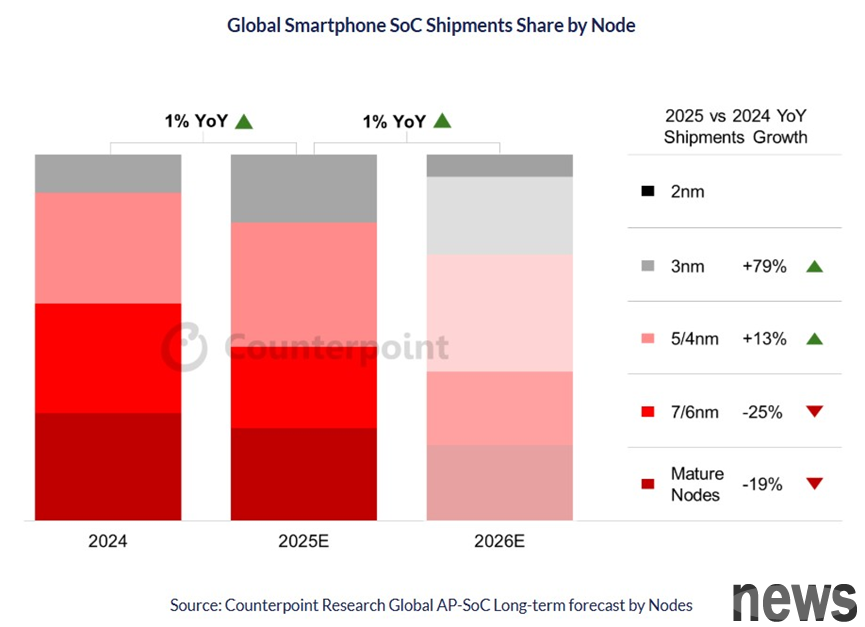
Counterpoint Research experienced analyst Parv Sharma said that the current market demand for device-side AI computing capabilities is driving chips towards smaller, stronger and more efficient processes. But this also leads to an increase in the overall SoC cost, including an increase in the price of wafers and semiconductor content. It is expected that by 2026, one-third of smart phone SoCs will enter 3 nm and 2 nm points, achieving an important milestone.
Parv believes that NTEC has scheduled a tape-out for 2 nanometers in the second half of the year, and will enter the volume in 2026. Apple, Qualcomm and Joint Development Corporation will launch the first wave of 2-nanometer flagship SoC by the end of 2026. In the early stage, the adoption will be mainly flag-line and high-level markets; the medium-level devices will gradually shift from 7/6 nanometers to 5/4 nanometers, and will transition to 3 nanometers in a few years; the entry-level 5G SoC will be upgraded from 7/6 nanometers to 5/4 nanometers, while the LTE SoC will be moved from mature to 7/6 nanometers.
Brady Wang, Associate Research Director of Counterpoint Research, expects that by 2025, smart phone SoCs with NT$5 nanometers and below (including 3 nanometers and 2 nanometers) will account for 87% of the market, and will increase to 89% in 2028. Major crystal-free circular-circuit manufacturers, such as Apple, Qualcomm and Joint Development, all rely on the leading process of TECHNOLOG.
However, Google Tensor and Samsung Exynos are still manufactured by Samsung. Although Samsung's 3-nanometer yield is facing challenges, leading to the smartphone market's delay, it will focus on 3-nanometer and 2-nanometer nodes and enter 2-nanometer production in 2026.
Brady Replenishment, from the middle to the future of flagship smart phones, will decide to be advanced below 4 nm. Except for Taiwan Electric, there are limited choices for OEM, only Samsung and SMIC International. SMIC supports HiSilicon SoC with 7 nanometers and supplies China-US geopolitical and EUV equipment export bans will be difficult to expand to more advanced stages in the short term. If Samsung can quickly expand the production scale of 2 nanometers and 3 nanometers, or SMIC International can obtain EUV machines, it will have the opportunity to challenge the leading position of telco.
Extended reading: Transmission speed reaches 38Tbps! China's silicon photonic chip industry is expected to usher in a major breakthrough in three years? IPC announces renamed to the Global Electronics Association, opening a new chapter